定义
代理模式(Proxy Pattern) :给某一个对象提供一个代 理,并由代理对象控制对原对象的引用。
使用场景
- 需要表示一个对象整体或部分层次,在具有整体和部分的层次结构中,希望通过一种方式忽略整体与部分的差异,可以一致地对待它们。
- 让客户能够忽略不同对象层次的变化,客户端可以针对抽象构件编程,无须关心对象层次结构的细节。
UML 图
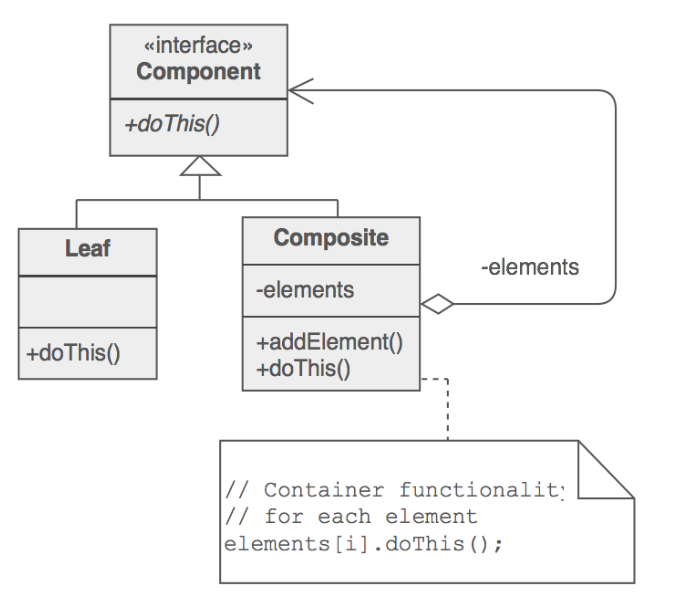
简单实现
例子
public abstract class Component {
protected abstract void operation();
protected void add(Component component) {
System.out.println("no add");
}
protected void remove(Component component) {
System.out.println("no remove");
}
protected void getChild(int i) {
System.out.println("no getChild");
}
}
public class LeafOne extends Component {
@Override
protected void operation() {
System.out.println("LeafOne operation");
}
}
public class LeafTwo extends Component {
@Override
protected void operation() {
System.out.println("LeafTwo operation");
}
}
public class Composite extends Component {
private List<Component> list;
public Composite(List<Component> list) {
this.list = list;
}
@Override
protected void operation() {
for (Component component:list) {
component.operation();
}
}
@Override
protected void add(Component component) {
list.add(component);
}
@Override
protected void remove(Component component) {
list.remove(component);
}
@Override
protected void getChild(int i) {
list.get(i);
}
}
客户端调用
public class CompositeMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("CompositeMain RUNNING");
Component leafOne = new LeafOne();
Component leafTwo = new LeafTwo();
Component composite = new Composite(new ArrayList<>());
composite.add(leafOne);
composite.add(leafTwo);
Component root = new Composite(new ArrayList<>());
root.add(leafOne);
root.add(leafTwo);
root.add(composite);
root.operation();
}
}
结果
CompositeMain RUNNING
LeafOne operation
LeafTwo operation
LeafOne operation
LeafTwo operation
类图
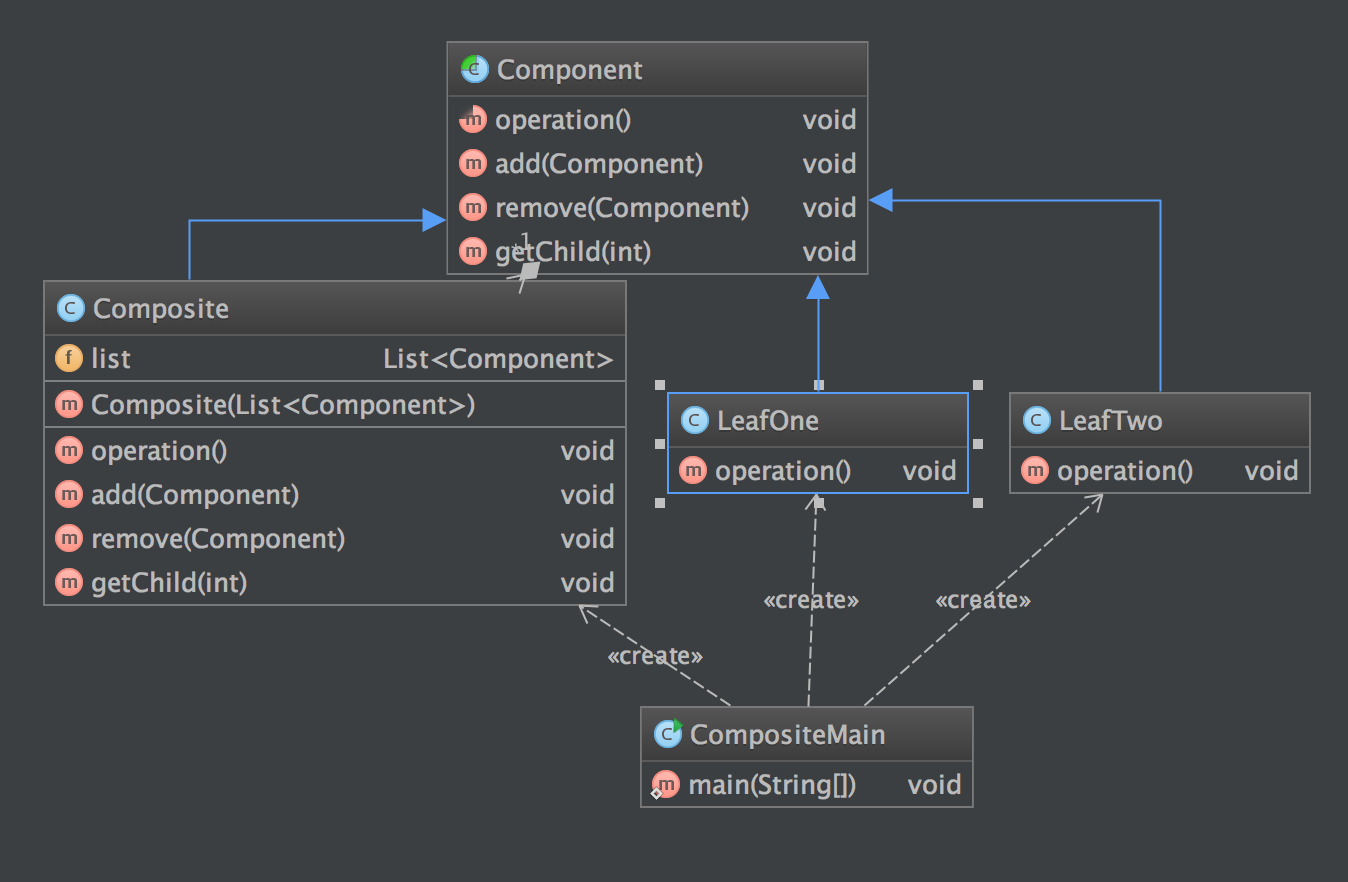
优缺点
- 优点
- 可以清楚地定义分层次的复杂对象,表示对象的全部或部分层次,使得增加新构件也更容易。
- 客户端调用简单,客户端可以一致的使用组合结构或其中单个对象。
- 定义了包含叶子对象和容器对象的类层次结构,叶子对象可以被组合成更复杂的容器对象,而这个容器对象又可以被组合,这样不断递归下去,可以形成复杂的树形结构。
- 更容易在组合体内加入对象构件,客户端不必因为加入了新的对象构件而更改原有代码。
- 缺点
- 使设计变得更加抽象,对象的业务规则如果很复杂,则实现组合模式具有很大挑战性
## 总结
- 使设计变得更加抽象,对象的业务规则如果很复杂,则实现组合模式具有很大挑战性
- 组合模式用于将多个对象组合成树形结构以表示“整体-部分”的结构层次。组合模式对单个对象(叶子对象)和组合对象(容器对象)的使用具有一致性。
- 组合对象的关键在于它定义了一个抽象构建类,它既可表示叶子对象,也可表示容器对象,客户仅仅需要针对这个抽象构建进行编程,无须知道他是叶子对象还是容器对象,都是一致对待。
- 组合模式虽然能够非常好地处理层次结构,也使得客户端程序变得简单,但是它也使得设计变得更加抽象,而且也很难对容器中的构件类型进行限制,这会导致在增加新的构件时会产生一些问题。
## 参考
> http://blog.csdn.net/hguisu/article/details/7530783
> http://www.cnblogs.com/chenssy/p/3299719.html
> 『head first 设计模式』